Surface Plate on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 A surface plate is a solid,
A surface plate is a solid,
Iso standard defines ISO8512-2 for granite surface plates, but it seems the current in use is still dating back 1990.
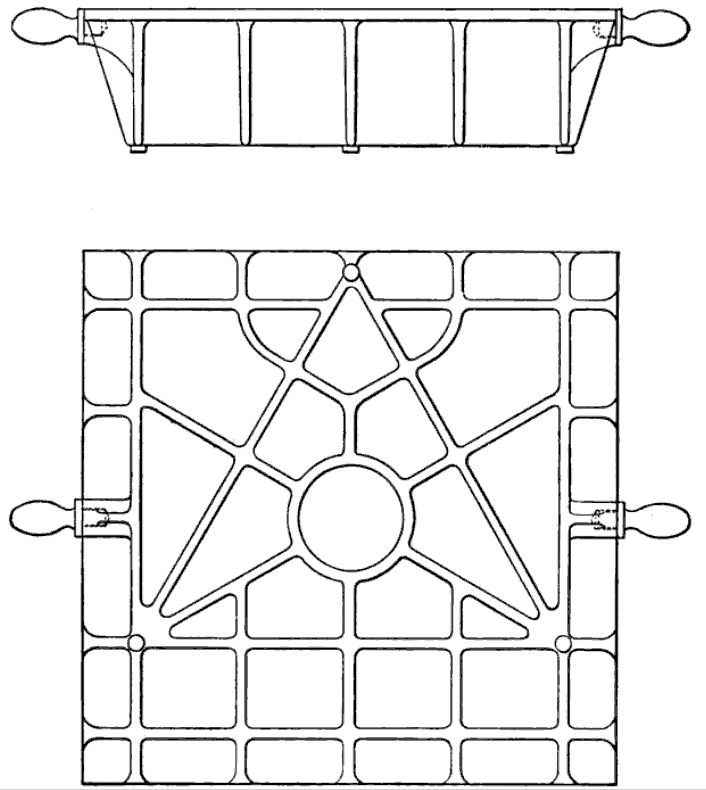 Prior to World War II, almost all surface plates were made from ribbed
Prior to World War II, almost all surface plates were made from ribbed
Two surface plates made by Whitworth
* * {{Authority control Metalworking measuring instruments Quality control

 A surface plate is a solid,
A surface plate is a solid, flat
Flat or flats may refer to:
Architecture
* Flat (housing), an apartment in the United Kingdom, Ireland, Australia and other Commonwealth countries
Arts and entertainment
* Flat (music), a symbol () which denotes a lower pitch
* Flat (soldier), ...
plate
Plate may refer to:
Cooking
* Plate (dishware), a broad, mainly flat vessel commonly used to serve food
* Plates, tableware, dishes or dishware used for setting a table, serving food and dining
* Plate, the content of such a plate (for example: ...
used as the main horizontal reference plane
In celestial mechanics, the plane of reference (or reference plane) is the plane used to define orbital elements (positions). The two main orbital elements that are measured with respect to the plane of reference are the inclination and the longi ...
for precision inspection, marking out Marking out or layout means the process of transferring a design or pattern to a workpiece, as the first step in the manufacturing process. It is performed in many industries or hobbies although in the repetition industries the machine's initial set ...
(layout), and tooling setup. The surface plate is often used as the baseline for all measurements to a workpiece, therefore one primary surface is finished extremely flat with tolerances below per 2960 mm for a grade 0 plate. Surface plates are a common tool in the manufacturing industry and are often fitted with mounting points so that it can be an integrated structural element of a machine such as a coordinate-measuring machine
A coordinate measuring machine (CMM) is a device that measures the geometry of physical objects by sensing discrete points on the surface of the object with a probe. Various types of probes are used in CMMs, the most common being mechanical and l ...
, precision optical assembly, or other high precision scientific & industrial machine. Plates are typically square or rectangular, although they may be cut to any shape.
Accuracy and grade
There are varying grades used to describe the accuracy of somemetrology
Metrology is the scientific study of measurement. It establishes a common understanding of units, crucial in linking human activities. Modern metrology has its roots in the French Revolution's political motivation to standardise units in Fran ...
equipment such as: AA, A, B, and Workshop grade. While workshop grade is the least accurate, all grades of surface plates are held to a high degree of flatness.
Surface plates must be calibrated
In measurement technology and metrology, calibration is the comparison of measurement values delivered by a device under test with those of a calibration standard of known accuracy. Such a standard could be another measurement device of known ...
regularly to ensure that chipping, warping, or wear has not occurred. A common problem is wear to particular areas, such as that caused by the frequent use of a tool in one place (such as a height gauge
A height gauge is a measuring device used for determining the height of objects, and for marking of items to be worked on.
These measuring tools are used in metalworking or metrology to either set or measure vertical distances; the pointer is s ...
), that causes an uneven surface and reduces overall accuracy of the plate, this may be greatly accelerated if abrasive dust is present. Tools and workpieces may also cause damage when dropped on the surface plate. Also, damage can be caused when swarf and other debris have not been removed. This will result in erroneous measurements. Damage to the plate can be corrected only by resurfacing, which requires specialised techniques and equipment depending on the grade of the plate.
History
Unlike most mechanical precision instruments, surface plates do not derive their precision from more-precise standards. Instead they originate precision by application of the principle of "automatic generation of gages". In this process, three approximately flat surfaces are progressively refined to precise flatness by manually rubbing them against each other in pairs with colouring matter in between, and then hand-scraping the high points. Any errors of flatness are removed by this scraping, since the only stable, mutually conjugate surface shape is a plane. The importance of the high-precision surface plate was first recognised byHenry Maudslay
Henry Maudslay ( pronunciation and spelling) (22 August 1771 – 14 February 1831) was an English machine tool innovator, tool and die maker, and inventor. He is considered a founding father of machine tool technology. His inventions were ...
around 1800. He originated the systems of scraping a cast-iron plate to flatness, rubbing marking blue between pairs of plates to highlight imperfections, and of working plates in sets of three to guarantee flatness by avoiding matching concave and convex pairs.
Joseph Whitworth
Sir Joseph Whitworth, 1st Baronet (21 December 1803 – 22 January 1887) was an English engineer, entrepreneur, inventor and philanthropist. In 1841, he devised the British Standard Whitworth system, which created an accepted standard for scr ...
, born in 1803, had been an apprentice with Maudslay from 1825 but had left by the time he started his own business in 1833. He described this process to the British Association
The British Science Association (BSA) is a charity and learned society founded in 1831 to aid in the promotion and development of science. Until 2009 it was known as the British Association for the Advancement of Science (BA). The current Chie ...
in 1840 in his paper ''"On producing True Planes or Surfaces on Metals"''—as he related during his chairman's address in 1856 at the inaugural meeting of the British Institute of Mechanical Engineers in Glasgow. His 1840 paper, and his past work for Maudslay, has led to some writers claiming Whitworth as the originator of the surface plate scraping technique, not Maudslay.
Plate material
Granite
Before theSecond World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, metal was the standard material used for surface plates, however, the war efforts of various countries put a strain on the availability of metal. A monument and metal shop owner (Wallace Herman) in Dayton, Ohio, along with his inventive employee Donald V. Porter, started using granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained (phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies undergro ...
in place of metal for his surface plates. Today most surface plates continue to be made of black granite, more accurately referred to as black diabase
Diabase (), also called dolerite () or microgabbro,
is a mafic, holocrystalline, subvolcanic rock equivalent to volcanic basalt or plutonic gabbro. Diabase dikes and sills are typically shallow intrusive bodies and often exhibit fine-graine ...
, with the more wear-resistant surface plates being made of quartz-bearing granite. The quartz content of these granite surface plates increases the wear resistance of the plate as quartz is a harder stone. Black granite is dominantly used in machine bases, granite accessories, and custom applications for its superior stiffness, excellent vibration damping, and improved machinability. Quartz-bearing granite (usually pink, white, or grey) is often made thicker than black granite to provide equal load-bearing capabilities of the types of material used for surface plates, as it is not as stiff as black granite.
Damage to a granite surface plate will usually result in a chip but does not affect the accuracy of the overall plane. Even though it is chipped, another flat surface can still make contact with the undamaged portion of a chipped surface plate, whereas damage to a cast-iron plate often raises the surrounding material above the working plane causing inspected objects to no longer sit parallel to the surface plate.
Granite is also inherently stable, is non-magnetic, has excellent vibration damping
In classical mechanics, a harmonic oscillator is a system that, when displaced from its equilibrium position, experiences a restoring force ''F'' proportional to the displacement ''x'':
\vec F = -k \vec x,
where ''k'' is a positive constan ...
characteristics, and will not rust.
On 3 August 1961, Federal Specification GGG-P-463B was issued to provide requirements in United States customary units
United States customary units form a system of measurement units commonly used in the United States and U.S. territories since being standardized and adopted in 1832. The United States customary system (USCS or USC) developed from English units ...
for igneous rock (granite) surface plates for use in precision locating layout, and inspection work. It encompassed new certification, recertification in the field, and recertification after resurfacing. GGG-P-463B was later revised and reissued on 12 September 1973 as GGG-P-463C, which provided common language and terms of classification for surface plate manufacturing and commerce. On 15 June 1977 an amendment was issued to the federal specification in order to include requirements in metric units
Metric units are units based on the metre, gram or second and decimal (power of ten) multiples or sub-multiples of these. The most widely used examples are the units of the International System of Units (SI). By extension they include units of el ...
.
Although GGG-P-463C was used extensively in American industry since its publication, the government did not issue any new revisions to keep up with advancements within industry. The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) decided to form a committee to revise the federal specification in accordance with modern technologies. Most notably, a more complete glossary was added with currently accepted definitions, and a new format was used that should be more familiar to current users of the Standard. ASME also recognised the need for updates to incorporate modern concepts such as traceability and measurement uncertainty that have undergone considerable development since 1973. In June 2013, ASME replaced Fed Spec GGG-P-463C with the American National Standard (ANS) ASME B89.3.7 – 2013 Granite Surface Plates.B89.3.7 Granite Surface PlatesIso standard defines ISO8512-2 for granite surface plates, but it seems the current in use is still dating back 1990.
Cast iron
 Prior to World War II, almost all surface plates were made from ribbed
Prior to World War II, almost all surface plates were made from ribbed cast iron
Cast iron is a class of iron–carbon alloys with a carbon content more than 2%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloy constituents affect its color when fractured: white cast iron has carbide impuriti ...
with the ribbing used to increase stiffness without incurring the weight of solid construction. The cast iron was aged
Ageing ( BE) or aging ( AE) is the process of becoming older. The term refers mainly to humans, many other animals, and fungi, whereas for example, bacteria, perennial plants and some simple animals are potentially biologically immortal. In ...
to reduce stress
Stress may refer to:
Science and medicine
* Stress (biology), an organism's response to a stressor such as an environmental condition
* Stress (linguistics), relative emphasis or prominence given to a syllable in a word, or to a word in a phrase ...
in the metal in an effort to decrease the likelihood of the plate twisting or warping over time.
Cast-iron surface plates are now frequently used on production floors as a tool for lapping
Lapping is a machining process in which two surfaces are rubbed together with an abrasive between them, by hand movement or using a machine.
Lapping often follows other subtractive processes with more aggressive material removal as a first step ...
granite surface plates to achieve certain grades of accuracy. The metal allows itself to be impregnated with the lapping media over a large flat surface.
Despite a fall in popularity among machine shops, cast iron remains the most popular material for master surfaces (different use from a surface plates) among laboratory metrologist
Metrology is the scientific study of measurement. It establishes a common understanding of units, crucial in linking human activities. Modern metrology has its roots in the French Revolution's political motivation to standardise units in Fran ...
s, machine builders, gauge makers, and other high-accuracy industries that have a requirement for gauging flatness. Cast iron that has been properly cast is more dimensionally and geometrically stable over time than granite or ceramics, is more easily worked to a higher grade of flatness, and provides a better bearing surface to assist the creation of other master standards. These specialized surface plates are produced in sets of three, by the company that will be using them, so the plates may be regularly verified and refined, including by the Whitworth three plate method, without the need to send them out to be reconditioned. Despite its high stability, cast iron remains unsuitable for use as a normal surface plate in high-tolerance production applications because of thermal expansion. The nature and use of a master surface, by contrast, already necessitates expensive measures to control temperature regardless of material choice, and cast iron becomes preferable.
Cast iron, unlike granite, has very uniform optical properties and, unlike glass or ceramic, very small light penetration depth which makes it favorable for certain optical applications.
Glass
Glass
Glass is a non-crystalline, often transparent, amorphous solid that has widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in, for example, window panes, tableware, and optics. Glass is most often formed by rapid cooling (quenching) of ...
is an alternative material and was used during World War II when material and manufacturing capacity were in short supply. Glass can be suitably ground and has the benefit that it chips rather than raising a burr, which is a problem when using gray cast iron.
Accessories
The surface plate is used in conjunction with accessories such as asquare
In Euclidean geometry, a square is a regular quadrilateral, which means that it has four equal sides and four equal angles (90-degree angles, π/2 radian angles, or right angles). It can also be defined as a rectangle with two equal-length adj ...
, straight edge
Straight edge (sometimes abbreviated sXe or signified by XXX or X) is a subculture of hardcore punk whose adherents refrain from using alcohol, tobacco, and other recreational drugs, in reaction to the excesses of punk subculture. For some, thi ...
, gauge blocks
Gauge blocks (also known as gage blocks, Johansson gauges, slip gauges, or Jo blocks) are a system for producing precision lengths. The individual gauge block is a metal or ceramic block that has been precision ground and lapped to a specific ...
, sine bar
A sine bar consists of a hardened, precision ground body with two precision ground cylinders fixed at the ends. The distance between the centers of the cylinders is precisely controlled, and the top of the bar is parallel to a line through the ce ...
, sine plate, dial indicator, parallels, angle plate
An angle plate is a work holding device used as a fixture in metalworking.
Angle plates are used to hold workpieces square to the table during marking out operations. Adjustable angle plates are also available for workpieces that need to be inc ...
, height gauge
A height gauge is a measuring device used for determining the height of objects, and for marking of items to be worked on.
These measuring tools are used in metalworking or metrology to either set or measure vertical distances; the pointer is s ...
, etc.
Calibration of surface plates
Granite surface plate calibration should be performed routinely to maintain proper flatness and ensure measurement accuracy over time. The intervals between calibrations depends on the environment where the surface plate is located. When needed, lapping or resurfacing is provided to bring measurements within grade guidelines. This procedure involves polishing the surface with an abrasive paste to remove all unwanted material. Granite surface plate calibration also includes cleaning and a light polishing.References
Further reading
*Society of Manufacturing Engineers, (1991). ''Fundamentals of Tool Design''. Dearborn, Michigan: Society of Manufacturing Engineers. * *External links
*Two surface plates made by Whitworth
* * {{Authority control Metalworking measuring instruments Quality control